CLOUD STUDIES
PRIX ARS ELECTRONICA 2021 – Artificial Intelligence & Life Art – Golden Nica
Authors:
Forensic Architecture (FA)
→ Artwork Video
→ Class Presentation PPT
Abstract:
Civil society rarely has privileged access to classified information, making the information that is available from ‘open sources’ crucial in identifying and analyzing human rights violations by states and militaries. The wealth of newly-available data—images and videos pulled from the open source internet—around which critical new methodologies are being built, demands new forms of image literacy, an ‘investigative aesthetics,’ to read traces of violence in fragmentary data drawn from scenes of conflict and human rights violations. The results of these new methodologies have been significant, and Forensic Architecture (FA) has been among the pioneers in this field, as open source investigation (OSI) has impacted international justice mechanisms, mainstream media, and the work of international human rights NGOs and monitors. The result has been a new era for human rights: what has been called ‘Human Rights 3.0.’
In Forensic Architecture’s work, physical and digital models are more than representations of real-world locations—they function as analytic or operative devices. Models help us to identify the relative location of images, camera positions, actions, and incidents, revealing what parts of the environment are ‘within the frame’ and what remains outside it, thereby giving our investigators a fuller picture of how much is known, or not, about the incident they are studying.
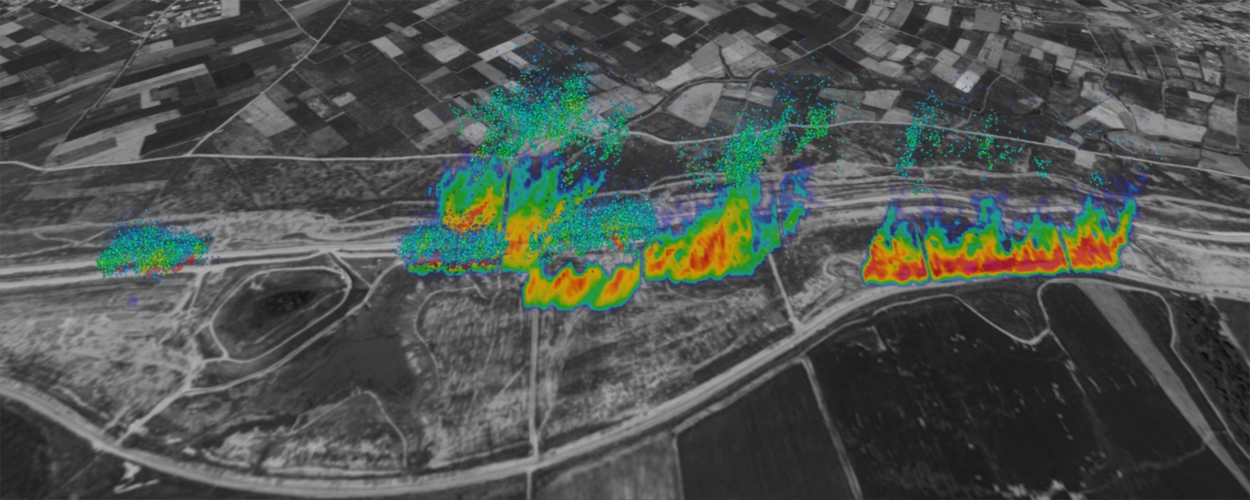
There remain, however, modes of violence that are not easily captured even ‘within the frame.’ Recent decades have seen an increase in airborne violence, typified by the extensive use of chlorine gas and other airborne chemicals against civilian populations in the context of the Syrian civil war. Increasingly, tear gas is used to disperse civilians (often gathered in peaceful protest), while aerial herbicides destroy arable land and displace agricultural communities, and large-scale arson eradicates forests to create industrial plantations, generating vast and damaging smoke clouds. Mobilized by state and corporate powers, toxic clouds affect the air we breathe across different scales and durations, from urban squares to continents, momentary incidents to epochal latencies. These clouds are not only meteorological but political events, subject to debate and contestation. Unlike kinetic violence, where a single line can be drawn between a victim and a ‘smoking gun’, in analyzing airborne violence, causality is hard to demonstrate; in the study of clouds, the ‘contact’ and the ‘trace’ drift apart, carried away by winds or ocean currents, diffused into the atmosphere. Clouds are transformation embodied, their dynamics elusive, governed by non-linear behavior and multi-causal logics.
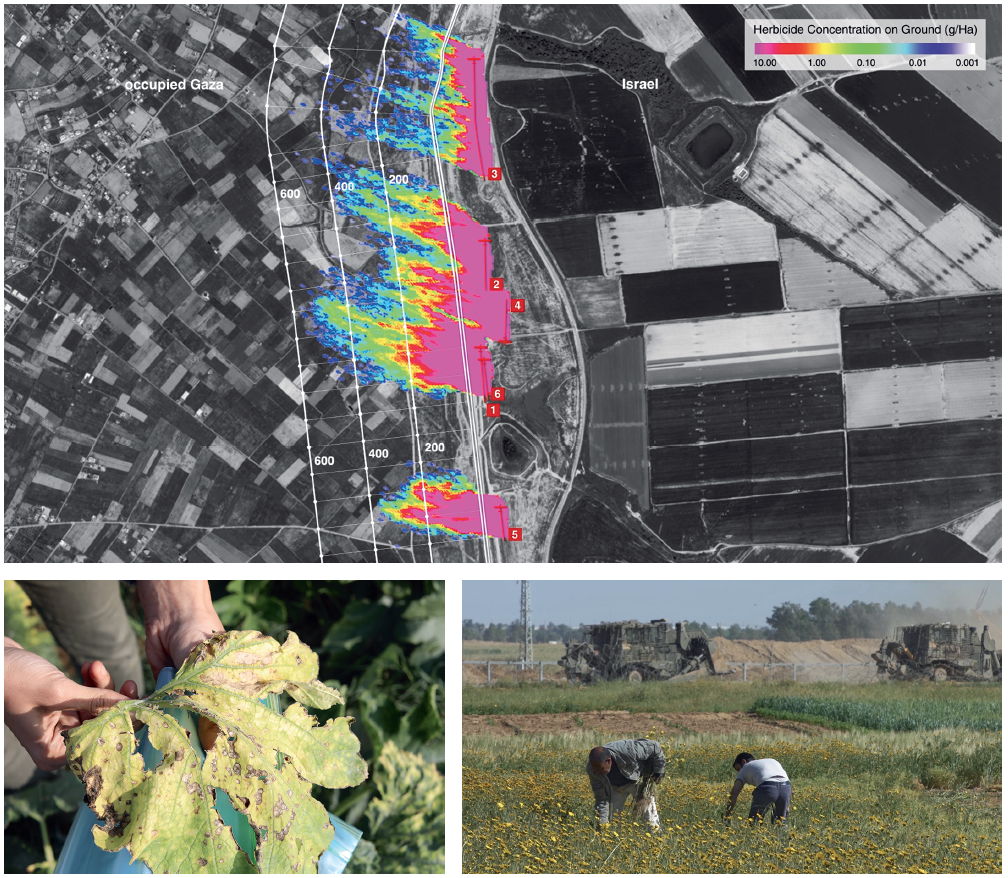
One response by FA has been to work with the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Imperial College London (ICL), world leaders in fluid dynamics simulation. Together, FA and ICL have pioneered new methodologies for meeting the complex challenges to civil society posed by airborne violence. The efficacy of such an approach in combatting environmental violence has already been demonstrated—FA’s investigation into herbicidal warfare in Gaza was cited by the UN—and has significant future potential, as state powers are increasingly drawn to those forms of violence and repression that are difficult to trace.
Cloud Studies brings together eight recent investigations by Forensic Architecture, each examining different types of toxic clouds and the capacity of states and corporations to occupy airspace and create unliveable atmospheres. Combining digital modelling, machine learning, fluid dynamics, and mathematical simulation in the context of active casework, it serves as a platform for new human rights research practices directed at those increasingly prevalent modes of ‘cloud-based,’ airborne violence. Following a year marked by environmental catastrophe, a global pandemic, political protest, and an ongoing migrant crisis, Cloud Studies offers a new framework for considering the connectedness of global atmospheres, the porousness of state borders and what Achille Mbembe terms ‘the universal right to breathe.’